Modbus RTU Module
This Lua module extends the functionality of the Barracuda App Server’s Modbus TCP Client by adding support for RTU (RS-232 and RS-485) communication. Essentially, it acts as a driver that enables the Modbus TCP Client to operate as a Modbus RTU Client. This module uses the UART API.
Note
The Lua module is included in the Xedge32 firmware but may be removed in later versions and provided as a separate module.
rtu=require"modbus.rtu".connect(port, config)
Create a Modbus RTU object.
Parameters:
The port and config parameters are sent to the esp32.uart() function. The config table takes one additional option, which optionally sets the Modbus TCP Client’s onclose configuration option.
Returns:
A new Modbus RTU object with the same API methods as provided by the Modbus TCP Client. The returned Modbus object is pre-configured for asynchronous cosocket mode, thus a callback is required for all method operations. See the example below for details.
Example:
local cfg = {
baudrate = 9600,
txpin = 42,
rxpin = 41,
onclose=function(err) trace("Serial Comm. Err.",err) end
}
-- Does not return errors, but may throw on incorrect settings
mb=require"modbus.rtu".connect(1,cfg)
local function mycallback(data, err, transaction, mb)
trace("table" == type(data) and ba.json.encode(data) or data, err)
end
local unitId=1 -- Optional for RS232, required for multidrop RS485.
mb:wholding(0, {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20}, unitId, mycallback)
mb:rholding(0, 20, unitId, mycallback)
The above callback prints the following, which are the Modbus server’s return values for the calls to mb:wholding() and mb:rholding(). The nil value at the end is from the err argument.
true nil
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20] nil
The above example configures the UART for RS232 mode or full duplex RS485. Half duplex (two-wire) RS485 communication requires collision detection and a chip such as ADM483 wired to the RTS GPIO pin. See the UART option rs485 for details. Half duplex RS485 mode can be configured as follows:
local cfg = {
baudrate = 9600,
txpin = 42,
rxpin = 41,
rtspin=40,
rs485=true
}
Modbus Test Bench:
(How to set up a two-wire RS485 Modbus test bench)
The following image shows our test bench.
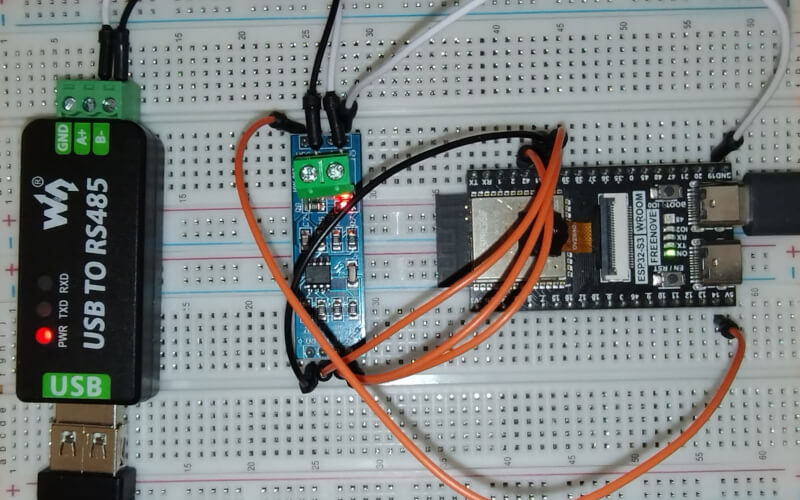
We used the following components for our test bench:
ESP32s3
ANMBEST MAX485 RS485 Transceiver Module
USB to RS485 converter
Modbus Slave Simulator running on Windows (connected to the USB to RS485 converter)
How to wire the components:
The following wiring matches the above configuration table.
Power Connections
VCC on MAX485 to 5V on ESP32
GND on MAX485 to GND on ESP32
Data Connections
DI on MAX485 to GPIO pin 42 on the ESP32: TX
RO on MAX485 to GPIO pin 41 on the ESP32: RX
Control Pins
RE and DE on MAX485 connected together, then to GPIO pin 40: RTS
RS485 Terminals
A and B terminals on MAX485 to the A and B lines on the USB to RS485 converter